Recent Posts
Categories
Stay Informed

In today’s complex digital landscape, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses are no longer sufficient. As businesses increasingly adopt cloud services, remote work, and mobile devices, the need for a more robust security framework has become critical. Zero Trust Security is a paradigm shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity.

What Is Zero Trust Security?
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity framework based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume everything inside an organization’s network is trustworthy, Zero Trust assumes that threats could come from both inside and outside the network.
This approach requires that every access request, whether coming from within the corporate network or outside, be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before granting access to any resources. In essence, Zero Trust eliminates the concept of a trusted internal network and treats all traffic as potentially dangerous.
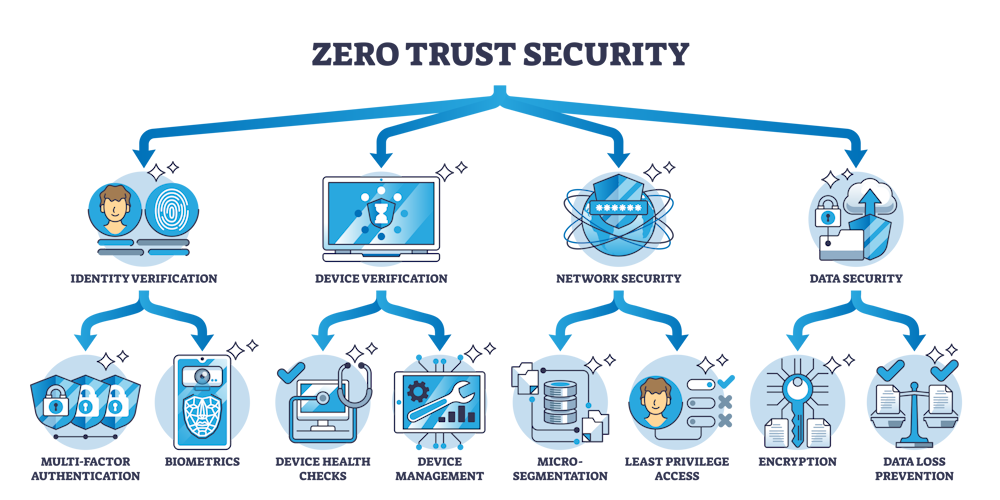
Principles of Zero Trust Security
Least Privilege Access
In a Zero Trust model, users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. This principle of least privilege reduces the risk of unauthorized access and limits the potential impact of a security breach.
Continuous Verification
Zero Trust requires ongoing verification of users, devices, and applications, even after they have been authenticated. This continuous monitoring helps detect and respond to suspicious activities in real-time.
Micro-Segmentation
Instead of relying on a single perimeter to protect the entire network, Zero Trust advocates dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. Each segment has its own security controls, ensuring that even if one segment is compromised, the breach doesn’t spread across the entire network.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a critical component of Zero Trust, adding an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., password, fingerprint, or a one-time code) before gaining access to resources.
Assume Breach Mentality
Zero Trust operates under the assumption that a breach has already occurred or could occur at any time. This mindset drives the need for robust monitoring, rapid incident response, and the implementation of fail-safe to minimize the damage from a potential breach.

Why Is Zero Trust Security Important?
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, with attackers often bypassing traditional perimeter defenses. Zero Trust addresses these challenges by assuming that threats can originate from anywhere, both inside and outside the network.
Increase in Remote Work
The rise of remote work has blurred the lines between internal and external networks, making it more difficult to secure organizational resources. Zero Trust provides a consistent security framework that applies regardless of where employees are located.
Cloud Adoption
As businesses move to the cloud, the traditional network perimeter becomes less relevant. Zero Trust ensures that cloud resources are protected by enforcing strict access controls and continuous monitoring.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries are subject to strict regulatory requirements for data protection. Zero Trust can help businesses meet these requirements by providing a comprehensive security framework that protects sensitive data and ensures compliance.

Implementing Zero Trust Security in Your Organization
Identify Critical Assets
Start by identifying the most critical assets within your organization, such as sensitive data, applications, and systems. These assets should be the primary focus of your Zero Trust strategy.
Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Ensure that robust IAM solutions are in place, including MFA and role-based access controls. These tools help enforce least privilege access and ensure that only authorized users can access critical resources.
Adopt Micro-Segmentation
Divide your network into smaller segments, each with its own security controls. This approach limits the lateral movement of attackers within the network and contains the impact of a breach.
Deploy Advanced Threat Detection
Use advanced threat detection and response tools to continuously monitor your network for suspicious activities. Automated threat detection and response can help identify and mitigate threats in real-time.
Establish a Zero Trust Culture
Educate your employees about the principles of Zero Trust and the importance of security best practices. A security-conscious culture is essential for the successful implementation of Zero Trust.

Conclusion
Zero Trust Security represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity. By adopting a “never trust, always verify” mentality, businesses can protect themselves against the increasingly sophisticated threats that traditional security models may fail to address.
For business owners, implementing Zero Trust is an investment in the long-term security and resilience of your organization. For IT professionals, it’s an opportunity to build a robust, adaptive security framework that meets the demands of today’s digital environment.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, Zero Trust Security provides a proactive, comprehensive approach to safeguarding your business’s most valuable assets. By embracing this model, you can reduce risk, enhance compliance, and ensure that your organization is well-equipped to handle the challenges of the modern digital landscape.



